Router 路由器
ip route manages routing tables: (Guide to IP Layer Network Administration with Linux)
- Find out Linux default gateway : ip route show
- Viewing the local routing table: ip route show table local
- Displaying the routing cache: ip route show cache
Output explanation of : ip route show
The network 10.220.209.0/24 is available on ens32 with a scope of link, which means that the network is valid and reachable through this device (ens32 ).
our all-important default route is expressed in the routing table with the word default. Note that any destination which is reachable through a gateway appears in the routing table output with the keywordviaThe scope of a route and the scope of an IP address: Understanding Linux network internals by Christian Benvenuti P785
site | valid only within this site (IPv6); Site-local address are supposed to be used within a site. Routers will not forward any packet with site-local source or destination address outside the site. This only applies to IPv6. There is no notion of site-local addresses in IPv4.
Link-local address are supposed to be used for addressing nodes on a single link. Packets originating from or destined to a link-local address will not be forwarded by a router.For proto kernel(routing protocol identifier of this route.), it is a route added automatically when you assign an address to an interface which is not /32. Lets say in your case, you assigned an address 111.211.3.193/26 to wlan0 (or some other in same subnet), kernel automatically adds route to whole subnet via this interface during auto-configuration. The only way to avoid this is assigning a /32 address to the interface.
A gateway is a network point that acts as an entrance to another network. A gateway is often associated with both a router, which knows where to direct a given packet of data that arrives at the gateway, and a switch, which furnishes the actual path in and out of the gateway for a given packet.
The routing policy database (RPDB) can be manipulated with the ip rule utility
label switching router 标签交换路由器/FIB (Forwarding Information Base): route cache
route cache has been removed from Linux 3.6/Route Path Selection
a Router’s primary purpose is to facilitate communication between networks --- 路由器的主要目的是促进网络之间的通信 As such, every router creates a boundary between two networks, and their main role is to forward packets from one network to the next
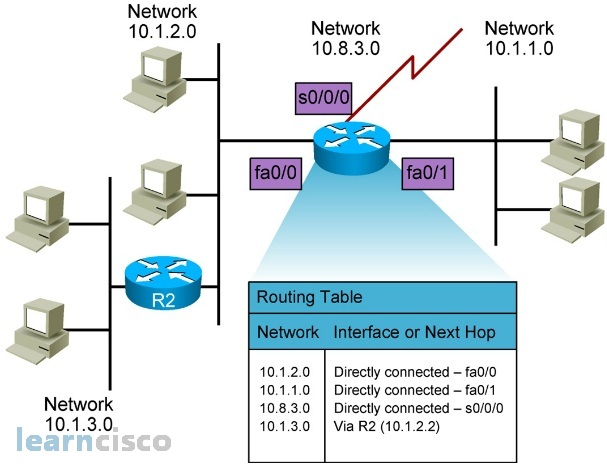
In order to forward packets between networks, a router must perform two functions: populate and maintain a Routing Table, and populate and maintain an ARP Table.
Routing metrics --- Optimal path selection depends on what is known as the cost to reach a destination across a certain path. Again, the cost of a path is made up of incremental costs for each hop along the path. The cost is also known as metric, and different routing protocols will consider different criteria in order to define the metric.
blackhole 10.0.7.0/24 proto bird
Notice there is a 10.0.7.0/24 blackhole, this subnet is used by the local pods on the worker node, communicating using the cali- interfaces; 表示发往10.0.7.0/24网段的报文都会被丢弃且不会回复源端。配置这条路由的原因是:这台机器上的Calico网络可分配的cidr是10.0.7.0/24,容器里访问同网段的其他IP时,配置该路由以避免报文被发到外部。
spine switch : 骨干交换机; assumed that the edge router in the infrastructure is the top of rack (TOR) switch: 假设基础设施中的边缘路由器是机架顶部(Tor)交换机