Next Permutation
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order). The replacement must be in-place, do not allocate extra memory.
Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.
1,2,3 → 1,3,2
3,2,1 → 1,2,3
1,1,5 → 1,5,1
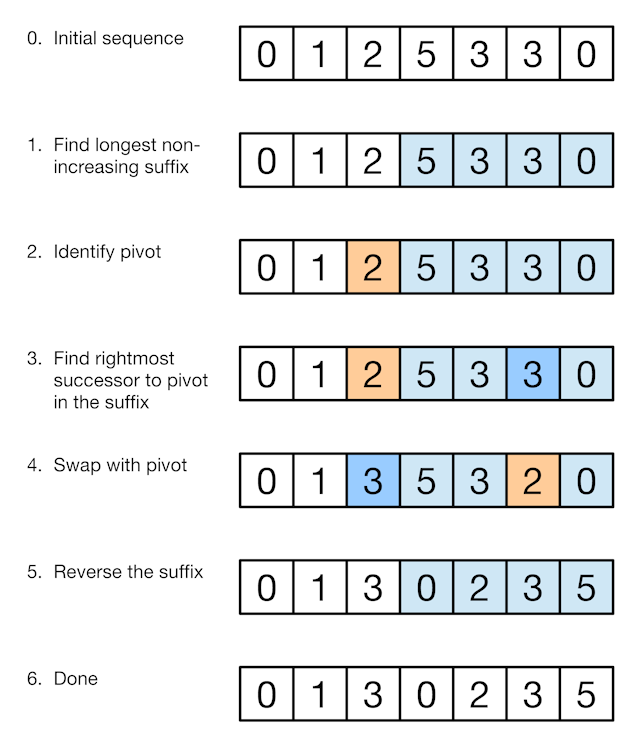
Java代码
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length<2)
return;
//scan from right to left, find the first element that is less than its previous one.
int p=0;
for(int i=nums.length-2; i>=0; i--){
if(nums[i]<nums[i+1]){
p=i;
break;
}
}
//scan from right to left, find the first element that is greater than p.
int q = 0;
for(int i=nums.length-1; i>p; i--){
if(nums[i]> nums[p]){
q=i;
break;
}
}
//rearrange it as the lowest possible order
if(p==0 && q==0){
reverse(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
return;
}
//swap p and q
int temp=nums[p];
nums[p]=nums[q];
nums[q]=temp;
//reverse elements [p+1, nums.length]
if(p<nums.length-1){
reverse(nums, p+1, nums.length-1);
}
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int left, int right){
while(left<right){
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left]=nums[right];
nums[right]=temp;
left++;
right--;
}
}